Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Noun?
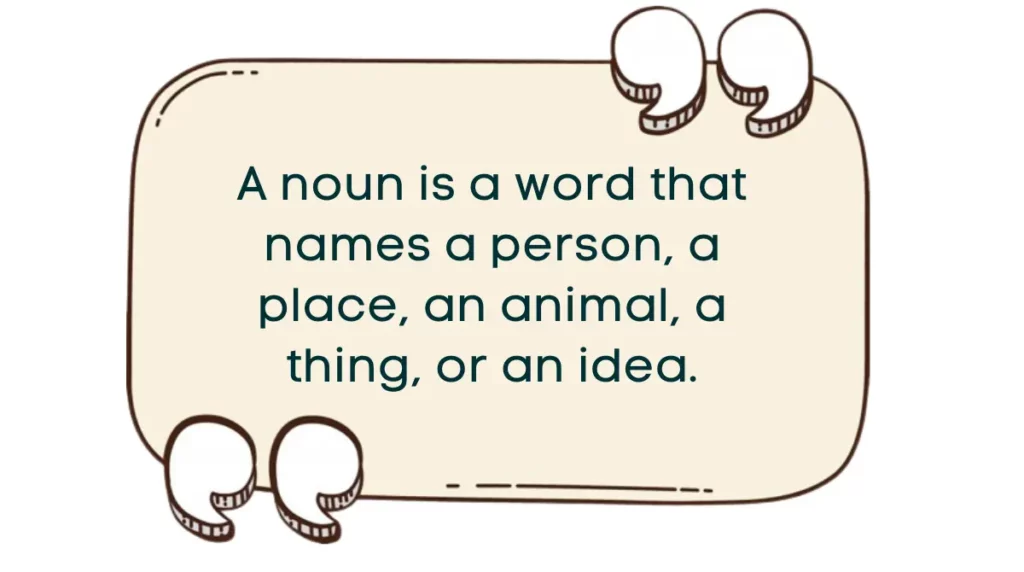
A noun names a person, place, thing or idea. Nouns give us words to talk about all people, places and things in our world.
Types of Noun
There are the main types of noun:
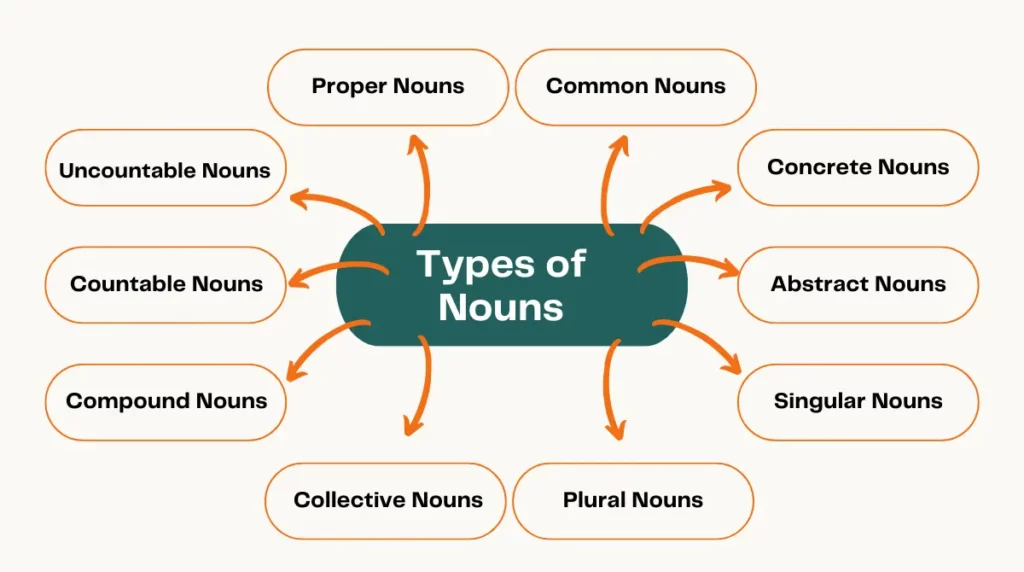
1. Common Nouns
Common nouns are general words that represent ordinary people, places, or things. They don’t specify a particular person, place, or thing.
Examples
- I saw a teacher in the hallway.
- Our country has a rich history.
- The furniture in the room is comfortable.
2. Proper Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names given to particular people, places, or things. They always start with a capital letter.
Examples
- Mr. Smith is our math teacher.
- We visited the Eiffel Tower in Paris.
- The Bible is a sacred text for many.
3. Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns are tangible, physical entities that can be perceived through the five senses. They include things you can see, hear, touch, smell, or taste.
Examples
- The desk in the office is wooden.
- The noise of the traffic kept me awake.
- She wore a dress made of soft cotton.
- The room smelled of her favorite perfume.
- An apple fell from the tree.
4. Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns represent concepts, qualities, or ideas that cannot be perceived through the senses. They express intangible things like emotions, states, or characteristics.
Examples
- Education is the key to success.
- The softness of the pillow was comforting.
- Timeliness is important for a good impression.
- Her face lit up with pure joy.
5. Collective Nouns
Collective nouns denote groups or collections of people, animals, or things. They refer to a singular entity made up of multiple individuals or items.
Examples
- The class went on a field trip.
- A herd of sheep grazed in the field.
- There’s a large pile of leaves in the yard.
6. Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are things that can be counted or made plural. They exist as individual, separate entities, allowing for the use of numerical values before them.
Examples
- I have three books on my shelf.
- She bought five new toys for her nephew.
- There are ten people waiting in line.
- The garden is filled with colorful flowers.
Read Most Common Ways to Form Plural Of A Noun
7. Non-count Nouns / Mass Nouns
In contrast, non-count nouns, also known as mass nouns, represent things that do not have distinct individuals or units. They cannot be made plural by adding an “s” or a number.
Examples
- I need to drink more water throughout the day.
- The room is filled with fresh, crisp air.
- She cooked a delicious pot of rice for dinner.
- His speech was full of profound wisdom.
8. Compound Noun
A compound noun is a type of noun that is made up of two or more individual words that are combined to form a new, single word. These words are typically connected by a hyphen or combined into one word.
Examples
- The bookshelf in my room is overflowing with novels.
- We visited a beautiful sunflower field during our road trip.
- The basketball game was intense, with the teams tied until the last minute.
How We Use Nouns in Sentences?
A noun can be used as the Subject of sentences, the object of the sentence, or with an adjective.
Noun as Subjects
In a sentence, the subject is the one doing the action. It could be a person, place, thing, or idea, setting the tone for the entire sentence. For example:
“The student (noun) studies (verb).” In this case, “the student” is the subject noun performing the action of studying.
Noun as Objects
The object, on the other hand, is the one receiving the action. It can be a person, place, thing, or idea, playing the role of the recipient. Take this example: “The teacher (subject noun) helps the boy (object noun).” Here, “the boy” is the object noun benefitting from the action initiated by “the teacher.”
Noun as Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe nouns, providing more details about them. They often come before the nouns they modify. For example: “The small dog barks loudly.” Here, “small” is an adjective describing the noun “dog,” giving us more information about the size of the dog.
Rules for Nouns
Plural Nouns
To indicate more than one of most nouns, add -s or -es to the singular form. For example:

- I have two books on my shelf.
- The cat chased three boxes around the room.
In both instances, the addition of -s or -es changes the noun from singular to plural. It indicates multiple items.
Possessive Nouns
Possessive nouns show ownership or belonging. To form possessive nouns, add ‘s or s’ apostrophe to the noun. Examples include:
- The girl’s jacket is hanging by the door.
- The dogs’ toys are scattered across the yard.
The use of ‘s or s’ apostrophe indicates that something belongs to the noun in question, whether it’s a singular or plural possessive.
Irregular Plurals
Some nouns have irregular plurals that don’t follow the regular -s or -es rule. Examples include:

- One child, many children
- One mouse, many mice
Nouns in Everyday Life
Nouns can represent the people, places and things around us – the building blocks of our daily life. For example:
- Common nouns: teacher, park bench
- Proper nouns: Mr. Johnson, Empire State Building
- Concrete nouns: desk, grass
- Abstract nouns: learning, beauty
- Collective nouns: class, litter
- Subject nouns: The boy
- Object nouns: kick the ball
- Possessive nouns: child’s toy
- Irregular plurals: mice, feet


